

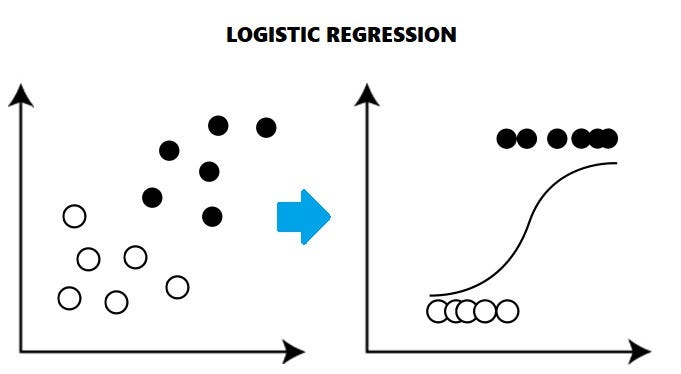
Logistic regression takes some inputs and calculates the probability of some outcome. For example, if a child has a temperature of 104F (40C) and they have a rash and nausea then the probability that they have chickenpox might be 80%.
Logistic regression uses a linear combination of the predictor variables to estimate the probability of the outcome being 0 or 1. This is why the word “regression” is in the name. Because the probability is calculated as a linear combination of the predictor variables, logistic regression models are relatively straightforward to interpret.
A rule of thumb in logistic regression, if the probability is > 50% then the decision is true. So in this case, the determination is made that the child has chickenpox.
Sources